The ARM64 RMP package can be run on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano as well as the Raspberry Pi with the Compute Module 5 when the system is sufficiently tuned.
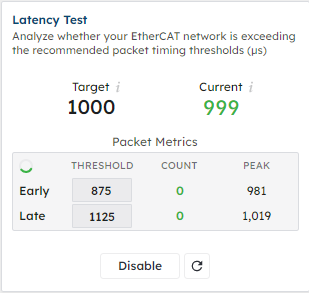
Running the RMPNetwork on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano at a 1kHz sample rate for 14 hours, the maximum send delta (the time between sending an EtherCAT datagram out to nodes on the network) reported by RapidSetupX was 1019 microseconds. A C# utility program for parsing the recorded timings reported that the RMP firmware delta had a maximum of 1018 microseconds and the RMPNetwork receive delta was 1019. Our default threshold for considering a packet as late is 12.5% of the sample period, which the Jetson Orin Nano was well under.
To simulate some mild activity on the Jetson Orin Nano running in parallel with the RMP, we also ran the commands:
sudo timeout 14h memtester 1500M 200
timeout 14h stress-ng --cpu 5 --cpu-load 10 --sched fifo --sched-prio 10 -t 14h
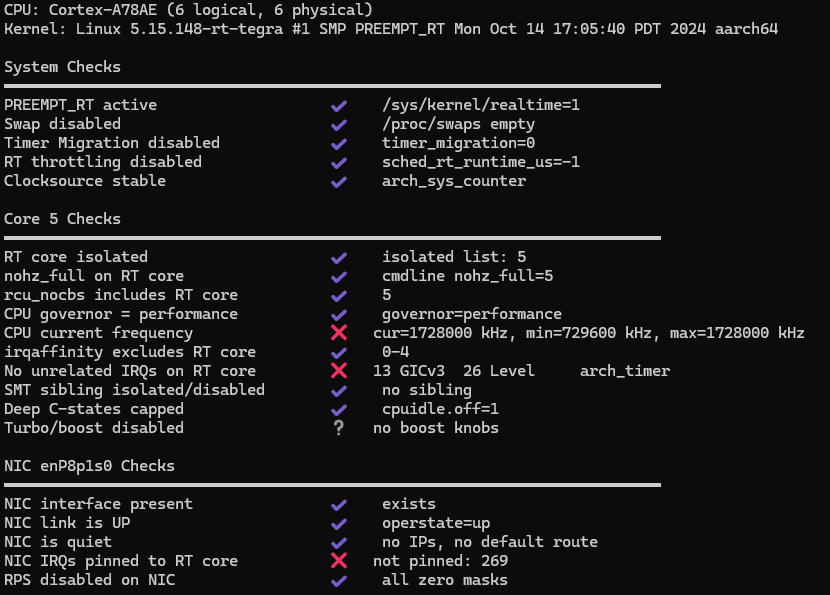
Using rmp-eval (GitHub - roboticsys/rmp-eval: An open-source Linux utility for evaluating a system's real-time performance and RMP EtherCAT suitability), we managed to tune the Jetson Orin Nano to have the configuration shown in the screenshot below. With regards to the pinning of IRQs, it seemed like we were unable to pin IRQs to an isolated CPU on this version of the Linux kernel, which may affect jitter on systems with a high workload on the non-isolated CPUs.
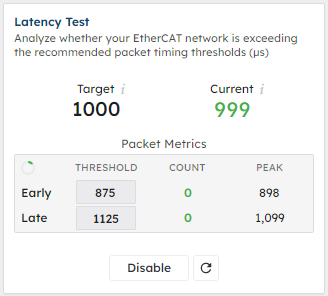
When running for 14 hours on the Raspberry Pi, the RMPNetwork’s maximum send delta was 1099 microseconds. The recorded maximum RMP firmware delta was 1109 microseconds, and the maximum network receive delta was 1101 microseconds.
The commands to simulate activity were:
timeout 14h memtester 2000M 200
timeout 14h stress-ng --cpu 3 --cpu-load 15 --sched fifo --sched-prio 10 -t 14h
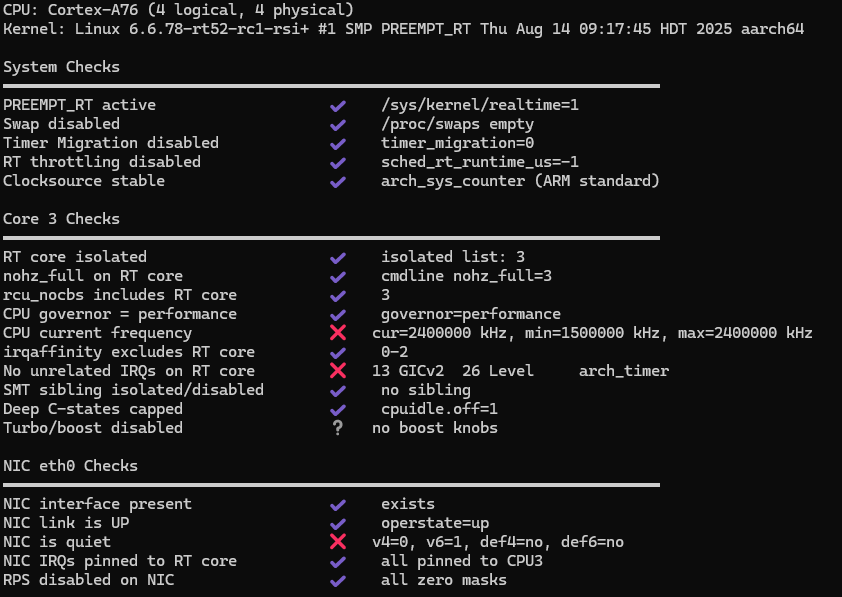
The configuration report from rmp-eval showed: